Everything You Need to Know About Genetic Testing (PGT) in IVF
What is Genetic Testing
Genetic testing, also known as Preimplantation Genetic Testing (PGT). Genetic Testing (PGT) is a technique used during IVF to examine an embryo’s chromosomes and detect specific genetic abnormalities. Using advanced technology like next-generation sequencing, PGT helps identify healthy embryos before transfer, increasing the chances of a successful pregnancy and reducing the risk of genetic disorders. Genetic testing are three main types:
- PGT‑A for aneuploidy (incorrect chromosome number).
- PGT‑M for monogenic (single gene) disorders.
- PGT‑SR for structural chromosome rearrangements.
This testing helps ensure that only healthy embryos are selected, reducing the risk of genetic diseases and increasing the likelihood of a successful pregnancy.
How Genetic Testing Works in the IVF Process?
Genetic testing is an advanced step integrated into the IVF process to analyse embryos before they are implanted. Here's how it typically works:
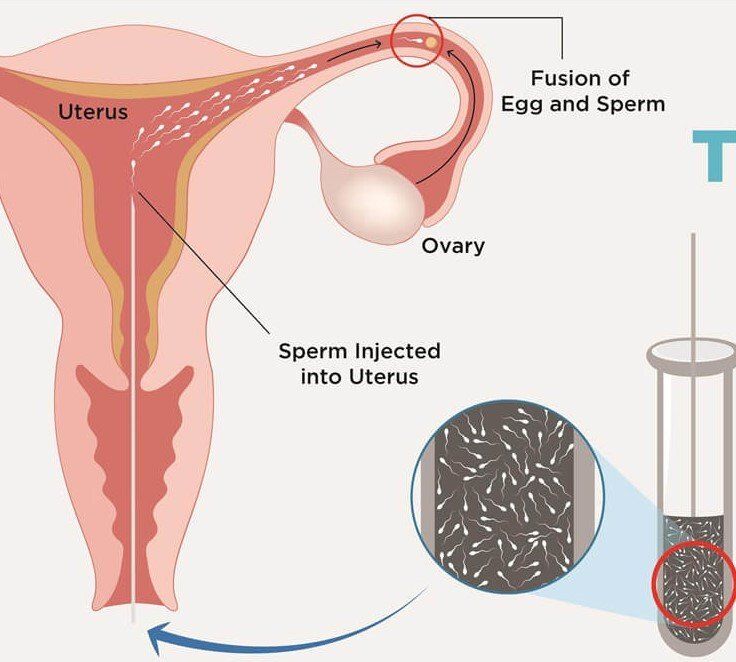
1. Ovarian Stimulation & Egg Retrieval
The IVF process begins with hormone medications to stimulate the ovaries to produce multiple eggs. These eggs are then retrieved in a short, outpatient procedure.
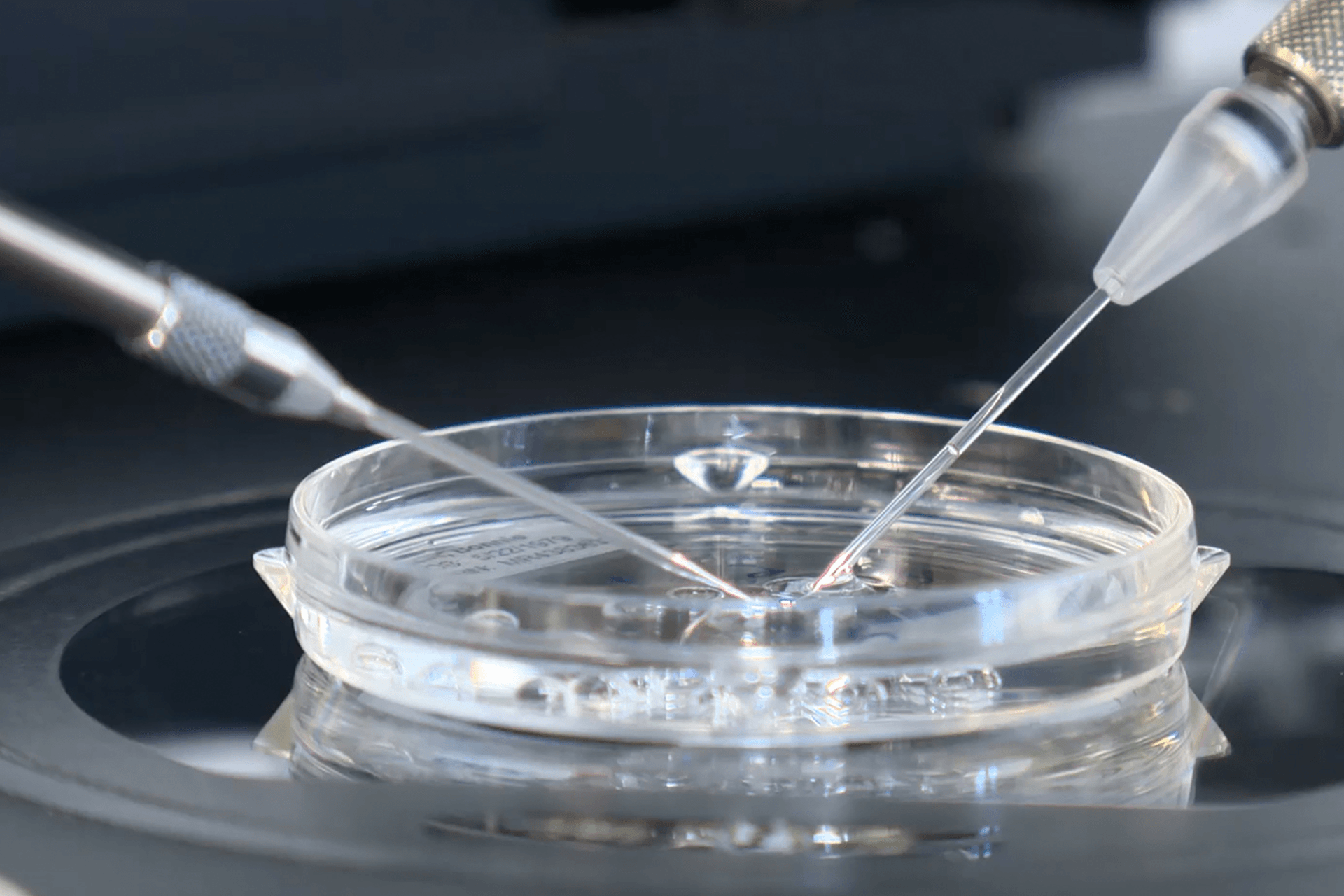
2. Fertilization in the Lab
The retrieved eggs are fertilized with sperm in a lab to create embryos. These embryos are monitored closely as they develop.
3. Embryo Development to Blastocyst Stage
Over the next 5–6 days, embryos grow to the blastocyst stage, which is when they have enough cells for safe testing without harming development.
4. Embryo Biopsy
At the blastocyst stage, a few cells are carefully removed from the embryo’s outer layer (which becomes the placenta). This procedure does not affect the part that will develop into the baby.
5. Genetic Analysis
The biopsied cells are sent to a specialized genetics lab. Using advanced techniques like Next-Generation Sequencing (NGS), the lab screens for chromosomal abnormalities (PGT-A), specific gene mutations (PGT-M), or structural rearrangements (PGT-SR).
6. Embryo Freezing
While testing is being completed (which usually takes about a week), embryos are cryopreserved (frozen) to preserve their quality.
7. Embryo Selection & Transfer
Once results are available, the fertility specialist selects the healthiest embryo(s) based on genetic results and prepares the patient for frozen embryo transfer (FET).
Who Should Consider Genetic Testing?
Genetic testing during IVF is especially helpful for individuals or couples with certain factors. You may consider it if you:
- Are over 35 (higher risk of chromosomal issues).
- Have had multiple miscarriages or failed IVF cycles.
- Have a family history of genetic disorders.
- Are known carriers of inherited conditions (e.g., cystic fibrosis).
- Have chromosomal rearrangements (like translocations).
- Want to avoid sex-linked diseases.
- Are interested in family balancing.
IVF Genetic Testing Pros and Cons
Pros of Genetic Testing:
- Better success rates: It helps pinpoint chromosomally normal embryos, which can lead to improved chances of implantation and pregnancy.
- Lower miscarriage risk: It reduces the likelihood of transferring embryos with chromosomal issues.
- Prevention of genetic disorders: It screens for specific inherited conditions in couples who are at risk (like cystic fibrosis or Tay-Sachs).
- Informed embryo selection: It boosts confidence in choosing the healthiest embryos for transfer.
- Family balancing option: In some cases, it allows for gender selection, particularly to prevent sex-linked disorders.
Cons of Genetic Testing:
- No guarantees: While it lowers risks, it doesn’t promise a healthy baby or a successful pregnancy.
- Limited detection: It may not catch all genetic conditions or rare mutations.
- Costly: It adds a significant financial burden to IVF and might not be covered by insurance.
- Embryo loss risk: There’s a slight chance that the biopsy could harm the embryo, although this is rare with today’s techniques.
- Ethical dilemmas: Choosing embryos based on genetics or gender can spark moral or cultural debates.
Limitations and Ethical Considerations
While genetic testing in IVF offers significant benefits, it also has limitations. PGT cannot detect every genetic or chromosomal issue, and while the risk of misdiagnosis is very low, less than 2% but it is not zero. The test does not guarantee the birth of a healthy baby. Because PGT doesn't assess every chromosome in detail, prenatal testing during pregnancy (such as amniocentesis or chorionic villus sampling) is still strongly recommended to confirm chromosomal structure and number.
In some cases, PGT may not yield results for certain embryos, or no chromosomally normal embryos may be available for transfer. This is more common in older patients, as the likelihood of chromosomal abnormalities increases with age.
Beyond clinical limitations, genetic testing also raises ethical considerations. Deciding which embryos to transfer, freeze, or discard based on genetic findings can be emotionally complex and ethically sensitive. The use of PGT for non-medical gender selection or personal preferences, often referred to as "family balancing," is a controversial topic in many cultures and countries. Additionally, the high cost of PGT may make it inaccessible for some, raising concerns about equity and fairness in fertility treatment. These considerations highlight the importance of thoughtful, personalized counselling when deciding whether to pursue genetic testing during IVF.
What is the Genetic Testing Pregnancy Cost?
The
cost of genetic testing during IVF or pregnancy can vary depending on several factors, including the type of test, the number of embryos or samples analysed, and the clinic or laboratory used. Testing such as PGT (Preimplantation Genetic Testing) is typically an additional expense not included in the base cost of IVF treatment.
Prenatal genetic tests like non-invasive prenatal testing (NIPT), amniocentesis, or chorionic villus sampling may also vary in cost depending on whether the pregnancy is considered high-risk and the extent of insurance coverage. Contact our fertility clinic to understand complete pricing & insurance details.
Schedule Your Consultation
Precision IVF Locations: Conveniently located in Frisco, Fort Worth and El Paso. However, we proudly welcome individuals and couples across USA, who are looking solutions for infertility problems.
Call us: 972-573-3200
Book an Appointment: Click here to book now
FAQ's on Preimplantation Genetic Testing
1. Is genetic testing safe for the embryo?
Yes, when performed by experienced professionals, the embryo biopsy used for PGT is considered safe and does not harm future development.
2. Is genetic testing mandatory for fertility treatment?
No, genetic testing is optional but strongly recommended in many cases.
3. Is genetic testing covered by insurance?
Insurance coverage for genetic testing varies based on the type of test, your specific policy, and the reason for testing. To learn more call us at 972-573-3200.
4. Where Precision IVF clinic located?
We welcome patienst from all ouver USA. However, Precision IVF clinic is located in multiple locations including, Frisco, Fort Worth & El Paso.